A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection within any part of the urinary system. This includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The infection comes from microbes or tiny organisms that require a microscope to be seen.
Bacteria cause most urinary tract infections, but some have been known to be caused by fungi and even rarer are those caused by viruses. Generally, these infections involve the parts of the urinary tract that are lower in the urinary system like the urethra and the bladder.
UTIs Are More Common Than You May Think
More women than men are at risk of UTI development, but overall, urinary tract infections are known to be among the most common of infections in humans. Experts rank a woman’s odds of getting a urinary tract infection as 50% at some point in her life. Many women suffer repeat infections, sometimes over years. For men, one in ten will experience a UTI in their lifetime.
The Three Types of UTIs
Cystitis
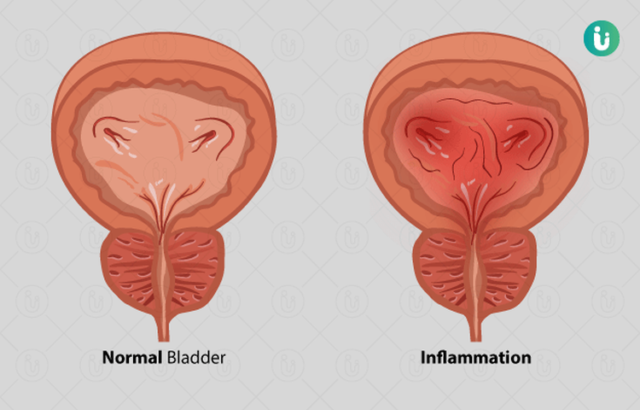
Each type of UTI has a different name that depends on where in the urinary tract it develops. Cystitis, for instance, takes place in the bladder. You might feel as though you need to urinate frequently or that urinating is painful. Lower belly pain goes along with cystitis, as does urine that is bloody or cloudy.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a urinary tract infection in the kidneys. This type of UTI is more serious. It can cause chills, fever, vomiting, nausea, and pain located in the upper side or back.
Urethritis

Urethritis, as the name suggests, is located in the urethra. This is the tube carrying urine from within the bladder to outside your body. In this condition, it becomes irritated and inflamed. Urethritis can lead to discharge and burning while urinating.
What Causes a Urinary Tract Infection?
Bacteria from inside the large intestine, including such varieties as E. coli, are capable of getting out from the anus and into the urethra. From that point, they can make their way up to the bladder. If the infection is not treated, it can then move on to infect the kidneys.
Bad Bathroom Hygiene

This spread of bacteria is a key reason behind doctors telling women to wipe themselves from front to back after using the bathroom. The urethra is closer to the anus in women, which makes them more susceptible to UTIs. Sexual intercourse can also introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
Genes
Genes can also be a cause behind some women’s increased likelihood of getting a urinary tract infection. Go to this site and learn how your genetics influence certain health conditions. Others are more prone to them because of the shapes of their urinary tracts. Diabetic women may suffer a higher risk of UTIs because of a weakened immune system, making them less capable of fighting off infections.
Age
Age is a factor that can increase the risk of getting a urinary tract infection, as older adults are more prone to getting them. Prolonged bed rest or reduced mobility, particularly after surgery, can be problematic in this regard as well. Previous UTIs boost the risk, as do prolonged use of a urinary catheter.
Pregnancy

Pregnancy can increase risk, too. Structures that are abnormally developed in the urinary system from birth are another factor. Other conditions increasing the risk in pregnant women include weakened immune systems, changes in hormones, multiple sclerosis, and such things that impact urine flow as strokes, kidney stones, or spinal cord injuries.
Symptoms of a UTI

Symptoms of urinary tract infections can include:
- A burning sensation when urinating.
- Frequent or intense urges to urinate despite little urine emerging when you try to go to the bathroom.
- Urine that is dark, cloudy, bloody, or that smells strange.
- Urine that resembles tea or cola.
- Pressure or pain in the back or lower part of the abdomen.
- A feeling of tiredness or shakiness.
- Chills or fever, which may indicate that the infection has reached the kidneys.
- Pelvic pain for women.
- Rectal pain for men.
Diagnosing a Urinary Tract Infection
When you suspect that you have a UTI, make an appointment with your doctor. You will undergo a review of the symptoms you are experiencing and receive a physical examination. Then, you will give a urine sample that will be tested for the bacteria that causes urinary tract infections.
The urine sample is required to be a sample that is caught clean. It must be collected mid-stream of urine, rather than catching it at the beginning of the flow. This assists in avoiding the collection of yeast or bacteria from the skin. When the sample is tested, your doctor looks for large numbers of white blood cells that indicate an infection.
If you suffer from frequent bouts of UTIs, your doctor may suspect a problem inside your urinary tract. In this case, a CT scan, an ultrasound, or an MRI may be taken to get a closer look. A cystoscope, a long, flexible tube, may be used as well to look within the bladder and the urethra. Other tests include an intravenous pyelogram or a cystoscopy.
How to Treat a UTI

If your doctor believes it’s necessary, antibiotics may be prescribed as they are among the most common treatments for UTIs. It’s necessary to take the entire course of prescribed medicines, even if you begin to feel better before you run out. While doing so, be sure to drink plenty of water to help your body flush the bacteria from your system.
You may also receive medication to help soothe the pain you are feeling. A heating pad, applied to the abdomen or back, can also be helpful for pain. When it comes to other home treatments, some recommend cranberry extracts. These have not been proven to actually help in the treatment, however, many continue to use them for UTI treatment.
For more information on UTI treatments, check out this helpful resource from Uqora.
What Happens When a UTI Goes Untreated?
Treatment of urinary tract infections is extremely important. When UTIs are left untreated, they spread, and become more and more severe. A lower urinary tract UTI is the easiest to treat, while other areas of the urinary system that become infected may be more difficult to heal. UTIs are also more likely to spread to the blood when this happens, which can cause sepsis, an event that is life-threatening.
How to Prevent UTIs

There are several things you can do to help prevent UTIs, particularly for women. Drinking plenty of water and other liquids will help both men and women. But for females, in particular, methods of avoiding UTIs include emptying the bladder immediately after intercourse, avoiding feminine products that might irritate the body, such as douches and deodorant sprays, and changing a birth control method from diaphragms or condoms that are unlubricated or treated with spermicide.
By avoiding these methods and practicing good bathroom hygiene, both men and women can prevent UTIs, accordingly to this website. If you believe you have a UTI or are experiencing symptoms of a UTI, always check in with your doctor before diagnosing yourself and starting treatment.