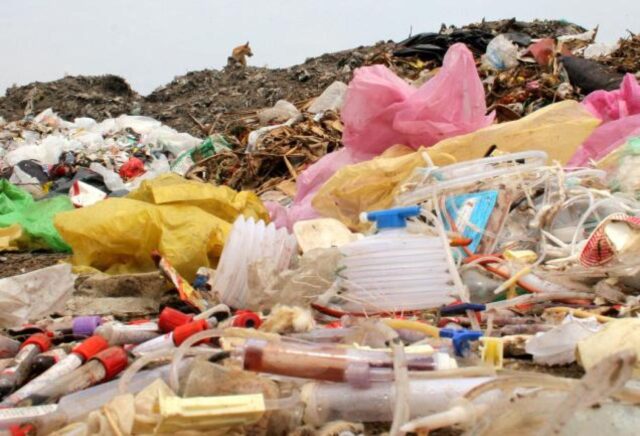

Do you have concerns about medical waste on our planet? With the mountains of medical waste being generated daily and disposed of improperly, it’s high time to look into the environmental impact it creates – and how you can reduce it.
Explore the implications of medical waste in this article and learn why taking better care of our planet is essential for all of us.
Sources of Medical Waste and Their Impact
This is any kind of waste generated by hospitals and healthcare professionals in the course of providing medical care. It can range from used bandages and needles to expired medications and used surgical equipment.
It can pose a significant risk to public health and safety if not handled and disposed of properly, as many of these materials are contaminated with infectious agents or harmful chemicals.
The sources of medical waste vary widely depending on the type of healthcare facility, but some common sources include:
- Medical sharps – including syringes, scalpels, needles, lancets, etc.;
- Animal by-products – blood products, body fluids, excretions;
- Cultures & stocks – used for laboratory tests;
- Human tissue & organs;
- Prescription drugs & expired medications;
- Unused/outdated supplies such as dressings, gloves, and gowns;
- Glassware & heavy metals that have been exposed to infectious agents;
- Chemical waste from laboratories or cleaning supplies.
Proper medical waste management is essential to prevent potential harm to public health and safety. This includes ensuring that medical waste is segregated, stored, transported, and disposed of properly, following strict guidelines and regulations to minimize the risk of exposure to infectious agents or harmful chemicals.
The environmental impact of medical waste is twofold: firstly it can cause direct physical harm if mishandled or improperly disposed of leading to a potential release into the environment through air emissions or water contamination from leaching into local waterways.
Secondly, there is an indirect risk due to increased human exposure over long periods which can lead to potential chronic illness caused by microbial agents like bacteria or fungi.
Strategies for Reducing Medical Waste
To reduce the environmental impact of medical waste, healthcare professionals should consider implementing the following strategies.
- Source Reduction: Healthcare facilities should prioritize reducing the amount of waste they generate by rethinking processes and procedures that create unnecessary products and packaging. Simple changes such as selecting medical supplies with minimal packaging or reusable containers can lead to significant reductions in waste production.
- Recycling: By recycling what is not needed for patient care, healthcare facilities can reduce their pressure on resources and lower their environmental footprint. Recyclable materials, such as glass bottles, plastic containers, and paper goods should be separate from hazardous materials like chemical disinfectants or radioactive substances.
- Proper Disposal: It is important for healthcare facilities to properly dispose of hazardous materials by local regulations. This means disposing of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and other materials in special containers for safe transport to an approved disposal facility. Medical wastes like sharps should also be disposed of according to manufacturer instructions or state law requirements and use sharps containers that are made from strong materials such as durable plastics or metals designed specifically for this purpose.
- Education: Healthcare providers can make a big difference by educating patients on ways they reduce their eco-footprint about medical treatments they receive by asking questions about recycling options, reusable personal care items, chemicals used in the process, and packaging materials used in the clinic setting.

Additionally, healthcare staff needs education regarding proper product handling; for example, single-use instruments should never be reused on different patients as this leads to greater waste production due to long-term sterilization costs associated with reprocessing them after use on a single patient.
Proper Disposal of Medical Waste
To reduce the amount of medical waste that can harm the environment, proper disposal methods should be used. The two most commonly used methods for disposing of medical waste are autoclave sterilization and incineration.
Autoclave sterilization uses intense heat and pressure to kill bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other organisms present in the waste. Incineration is the process of burning any combustible material via an incinerator connected to air pollution control equipment.
In some cases, when the amount of medical waste is too small to require special treatment or disposition methods (e.g., autoclaves or incinerators), local authorities may permit a “bulk pick up” service provided by a licensed professional company to manage the collection and disposal of hazardous materials such as syringes and needles, dialysis solutions bags/cartridges, gloves contaminated by blood or bodily fluids, cultures from Petri dishes/test tubes containing hazardous microbes, etc.
Other items that may require special handling include body parts from autopsy procedures or laboratory specimens which need special packaging processes followed by transportation by established guidelines about biohazards to avoid releasing any contained organisms into the environment upon disposal.
Regulations and Policies for Managing Medical Waste
The proper management of medical waste is essential for safeguarding public health and preventing environmental damage. Regulations and policies have been developed to ensure the safe transport, handling, treatment, and disposal of medical waste.
Regulations concerning medical waste are enacted at both the federal and state/local levels. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for setting provisions regarding the identification, segregation, packaging, labeling, and management of biomedical waste. Many states have laws that mirror EPA regulations but provide additional mandates specific to their jurisdictional requirements.
Healthcare facilities also benefit from taking proactive steps such as investing in environmentally-friendly disposal programs like autoclave sterilization systems which reduce or eliminate landfilling for some types of biomedical waste streams, ultimately minimizing their environmental impact on our planet.
By implementing these regulations and introducing additional supporting policies, healthcare providers can play a proactive role in helping protect our environment from the risks posed by chemical-laden discards like unused drugs or expired toxic chemicals used during patient care activities.
Conclusion
When it comes to general medical trash such as gauze or bandages, many materials like these are recyclable if disposed of in the appropriate bags or bins.

Additionally, whenever possible, opt for reusable medical supplies instead of single-use products that have to be thrown away. Taking these steps can help ensure our planet’s safety in light of growing global health concerns.








